Understanding LED Technology
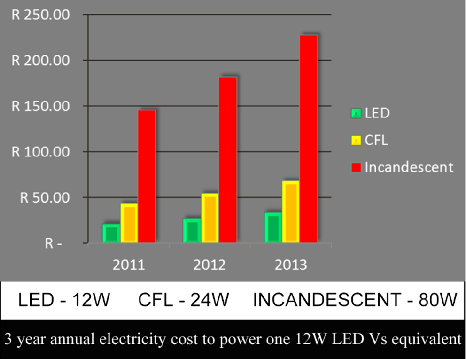
In today's climate of soaring electricity costs finding energy efficient alternatives is no longer solely about adopting environmentally friendly energy solutions, rather, there is a very real financial benefit to doing so.
Lighting contributes to around 50% of the average commercial building's electricity costs.
Light-emitting Diodes or "LEDs" are a semi-conductor light source which rely on electroluminescence (the use of electric current to generate light.) This differs from traditional solutions like incandescent bulbs, which use heat, and Compact Fluorescent Bulbs (CFCs), which use chemical reactions.
LEDs provide great efficiencies in reducing energy usage and costs.
Why LED Technology?
The benefits of LED technology include:
- Reduced energy consumption
- Longer lifetime
- Greater durability and reliability
- No harmful UV light
- No poisonous chemicals
- Improved robustness
- Reduced heat
All of these factors combine to lower both electricity consumption and light-bulb replacement costs, while providing stylish, aesthetically pleasing lighting solutions that have no harmful side-effects
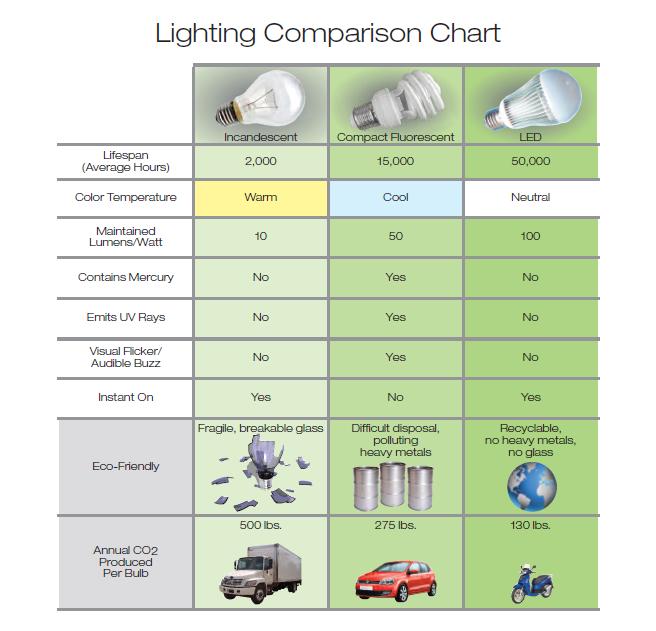
High powered LEDs achieve great efficiencies in emitting the same or similar light levels when compared to traditional solutions such as incandescent lights, Compact Fluorescent Lights (CFCs) or halogen lamps. Fundamentally, this is due to the fact that LEDs do not require heat or chemical reactions to produce light and the amount of electricity required is reduced dramatically, sometimes by up to 90%. Furthermore, the absence of heat also reduces the amount of degradation of the lamp over time, resulting in a much longer life-span of LED lights versus other solutions.
Finally, LED lights provide a "directional" light source by using optic lenses to bend light in a particular direction, whereas other solutions typically rely on reflectors to 'bounce' light off of a reflective surface into the desired direction.
Reflective light sources suffer from light degradation and lose efficiency as not 100% of the light actually reaches the desired point due to absorption by the reflective surface. Thus, the savings provided by LED lamps is three-fold, primarily on reduced energy consumption, secondly on the lower capital output required to replace lamps as time passes, and finally on the fact that LEDs achieve a higher light efficiency, meaning fewer lamps are required to light a given area, further reducing capital expenditure on the physical lamps.
Not all LEDs are equal
While LEDs provide greater efficiency than traditional lamps, they are certainly not created equal and there are varying levels of quality. The underlying factors related to LED quality can be broken into three broad categories: the Chipsets used, the power management modules, and finally, the heat dissipation technology used. These factors are incredibly important as low-quality LEDs often do not last even half the time a normal incandescent lamp would last, completely failing to deliver on the promises they make.
There are a few major players in the LED chipset market, namely Bridgelux, CREE, Epistar and Luxeon. While there are other chipset manufacturers, the brands listed above are internationally recognised as delivering high-quality, efficient chipsets. This is important as the chipset determines the quality of light not only in terms of brightness (lumens), but also in terms of lamp lifespan. Any serious LED vendor should offer at least one of the abovementioned Chipsets in their lamps
Power supply management is another extremely important factor to consider when purchasing LED lamps, especially in the South African context where our power supply is 220V.
An inability of an LED lamp to efficiently manage the power supply can result in the lamp burning out very quickly and becoming useless. This is often the case as many LED manufacturers design their solutions for the US or Asian markets where the power supply is only 110V and as a result, their lamps burn out very quickly.
Heat dissipation is another important aspect to consider as the amount of heat present in the system determines not only the quality of light output, but also the lifespan of the lamp itself. Almost all LED lamps have some sort of heat dissipation technology incorporated in the lamp.
Most solutions use a die-cast heat sink with a low surface area, while other solutions actually implement a fan to cool the LED. Die-cast solutions do little to reduce heat as most of the heat becomes trapped inside the lamp and the small amount of aluminium in the lamp cannot effectively dissipate the heat. Those solutions that use fans are typically even worse as, in addition to being a noisy solution, the fans often break long before the chipset lifespan is exhausted and the result is that the excess heat rapidly degrades the chipset which burns out very quickly due to excessive heat.
Our research has indicated the best heat dissipation technology is to use 100% aluminium with the largest surface area possible to effectively dissipate the heat.
All of these factors will affect the outcome of any attempt to replace existing lights with High-powered LED lamps and it is important for consumers to understand the facts before deciding on a solution.
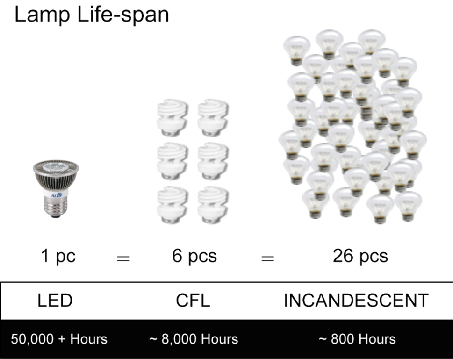
Lifespan: The image below illustrates the longevity of LED units vs incandescent and traditional lightbulbs
An important factor to note in this regard is that many LED vendors advertise the light output achieved by the chipsets only, which does not reflect the ACTUAL output, as light output degrades when one considers the impact of heat and the power supply and we strongly recommend you ask your LED vendor to clarify whether the advertised lumens are chipset or ACTUAL lumens.